St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
St. Jude Family of Websites
Explore our cutting edge research, world-class patient care, career opportunities and more.
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital Home

- Fundraising
Yongqiang Feng Lab
Exploring epigenetic control of T cell repertoire diversity and function
About the Feng Lab
T cells and other immune cells have the ability to distinguish and respond to diverse signals. We explore how tissue environment controls T cell diversity and function through epigenetic mechanisms. This process determines the adaptive immune response involved in transplant rejection, infection response, and tumor control. We use genetic tools and cutting-edge technologies to understand the normal and pathological function of T cells.
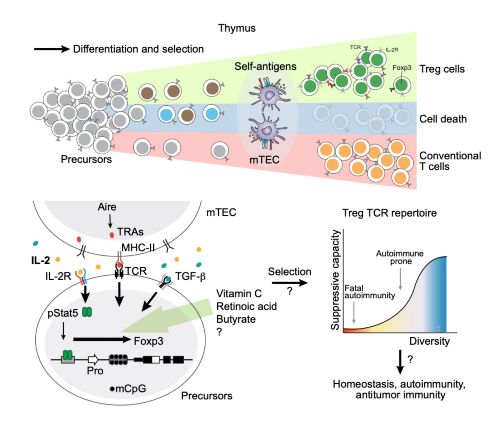
Our research summary
T cells and other immune cells have a natural ability to respond to numerous antigens, including self-antigens, tumor antigens, parasitic worms, bacteria, fungi, and viruses. At the root of that process is the remarkable ability of T cells to distinguish self from non-self, allowing the body to sustain immune homeostasis and providing the proper responses to numerous self and foreign antigens. The dysregulation of this mechanism underlies numerous human diseases, including cancer.
T cells are extremely heterogeneous, as shown by their diverse lineages that play distinct immunological functions as well as the astronomical antigen receptors that recognize numerous self and foreign antigens. The research in our laboratory primarily focuses on the balance between regulatory and conventional T cells. These two antagonizing cell types determine whether and how the immune system responds to self and foreign antigens.

Our research into T cell repertoire diversity and function aims to increase our understanding of how diverse antigen receptors of regulatory T cells are selected and sustained by genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. In addition, we investigate how the magnitude of this diversity governs the robustness and levels of immune tolerance involved in autoimmune diseases and antitumor immunity.
To identify novel factors and mechanisms controlling regulatory T cell diversity and immune suppressive function, we integrate cutting-edge technologies like CRISPR genome editing, single cell RNA sequencing, TCR profiling, proteomics, metabolomics, and epigenetics with innovative mouse genetic tools and disease models.
Because T cells play essential roles in numerous physiological and pathological settings, the research in our laboratory will lead to valuable insights into a variety of human immunological diseases, metabolic disorders, and cancer and may ultimately point the way to new therapeutic approaches.

Learn more
Immunity in the spotlight: how vaccinations and the immune system protect us
Researchers at St. Jude explain what immunity is and how it works.
Selected Publications
Contact us
Yongqiang Feng, PhD
Immunology
MS351, Room E7064
St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital
Memphis, TN, 38105-3678 USA GET DIRECTIONS

